Publication List
Book Chapter:
1. P. Roy & S. K. Srivastava (Eds.), Nanomaterials for Electrochemical Energy Storage Devices, 2019, Wiley. Link
2. P Roy, S Raj, SK Srivastava (2019), Nanostructured Metal Oxide, Hydroxide, and Chalcogenide for Supercapacitor Applications. In P. Roy & S. K. Srivastava (Eds.), Nanomaterials for Electrochemical Energy Storage Devices, 2019, Chapter 10, Wiley. Link
3. P. Roy (2017), Nanohybrid materials in the development of solar energy applications. In S.K. Srivastava & V. Mittal (Eds.), Hybrid Nanomaterials: Advances in Energy, Environment, and Polymer Nanocomposites, Chapter 3, Wiley. Link

81.
Chandni Das, Nibedita Sinha, Aathira Nair, Santanu Pal, Kavita Joshi,* Poulomi Roy*
Chlorophobic Iron Hydrogen Phosphite as OER-Active Electrocatalyst in Anion Exchange Membrane (Sea)Water Electrolysis
Small, 2025, 250578 (IF: 13)
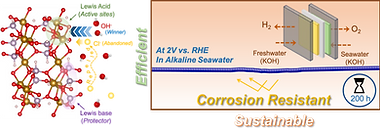
Seawater electrolysis is recognized as a promising technology to cater to the worldwide drive for sustainable hydrogen production; however, its practical viability is often hindered by the inevitable anode corrosion arising from the electrode side reactions owing to the presence of high chloride content which eventually degrade the electrode performance eventually. Herein, the design of unprecedented ammonium iron hydrogen phosphite (FeHPhi) along with a trace amount of Cu, is reported as the unique and much desired electrode material for seawater electrolysis due to its special chloride repellant nature along with great electrocatalytic activity toward water oxidation. The [HPO3]2− oxoanion as Lewis base in the structure effectively restricts chloride ions, while the Fe center acts as Lewis acid offering an active site for water oxidation, also well-supported theoretically. Leveraging this frustrated Lewis pair combination, the electrocatalyst achieves a high current density of 500 mA cm−2 at 344 mV overpotential in alkaline real seawater with impressive robustness to sustain for 200 h when operated under chlorine evolution reaction dominating region (>2 V). The electrocatalyst also demonstrates superior performance in anion exchange membrane freshwater and seawater electrolysis, demonstrating its potential applicability.
77.
Santanu Pal, Ekta Chaturvedi, Chandni Das, Nibedita Sinha, Tanbir Ahmed, Poulomi Roy*
NiFeMo layered triple hydroxide and MXene heterostructure for boosted oxygen evolution reaction in anion exchange membrane water electrolysis
Nanoscale, 2025, 17, 12094-12107 (IF: 5.1)
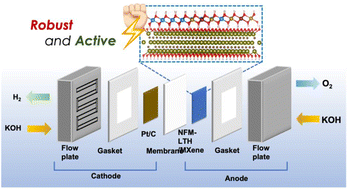
Interfacial engineering of heterostructures is quite beneficial for improving charge transfer efficiency at the interface. In this context, heterostructures of layered triple hydroxides (LTHs) and MXenes have shown great potential as OER electrocatalysts owing to their 2D–2D structure and unique physiochemical properties. Coupling LTHs with MXenes can potentially enhance their conductivity and stability, thereby boosting OER activity. In this study, we report a heterointerface between NiFeMo-LTH on Ti3C2Tx MXene, which exhibited superior catalytic activity and stability in alkaline freshwater and seawater, reducing the activation energy. Moreover, NiFeMo-LTH/MXene explored in alkaline anion exchange membrane water electrolyzer (AEMWE) achieved a current density of 750 mA cm−2 at 2.16 V cell voltage at an operating temperature of 60 °C with an energy efficiency of 60.5%.
79.
Santanu Pal, Nibedita Sinha, Chandni Das, Inderjeet Chauhan, Tanbir Ahmed, Poulomi Roy*
Enhanced Electrocatalytic Performances of NiCr Layered Double Hydroxides by Oxalate Intercalation in Anion Exchange Membrane Water Electrolysis
ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2025, 17, 37863–37878 (IF: 8.2)

Herein, NiCr-LDH has been developed, and its interlayer spacing has been considerably increased by oxalate intercalation. Such increased interlayer spacing allows easy access of hydroxides to a large number of electroactive sites and thereby boosts the electrocatalytic performances both for oxygen and hydrogen evolution reactions. Being very active toward both the electrocatalytic reactions, the oxalate-intercalated NiCr-LDH was further explored in an alkaline anion exchange membrane water electrolyzer (AEMWE), achieving 800 mA cm–2 at 1.88 V cell voltage at an operating temperature of 60 °C. In fact, the electrolyzer efficiency has been determined to be as high as 69.66%, and the calculated H2 production cost was found to be $0.97 per gasoline-gallon equivalent, which is well below the targeted cost by the Department of Energy, USA. The electrocatalyst was also examined in harsh alkaline media, like highly saline or seawater, which also indicated its ability to carry out sustainable seawater electrolysis, restricting chlorides to a great extent.
80.
Nibedita Sinha, Chandni Das, Santanu Pal, Poulomi Roy*
Energy-Saving H2 Production through H2S Electrolysis Accompanying Solid Sulfur Recovery Using a Ni3S2/Ni3N Heterostructure as the Electrocatalyst
ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2025, DOI: 10.1021/acsaem.5c01952 (IF: 5.8)
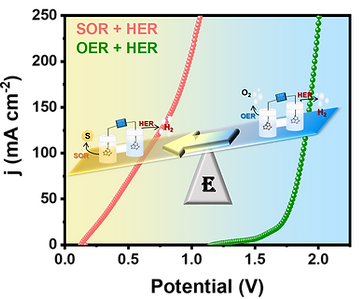
The thermodynamically feasible electrochemical sulfion oxidation reaction (SOR) is advantageous for degrading the toxic H2S pollutant into the value-added chemical sulfur but often suffers from catalyst passivation due to blockage of electroactive sites by accumulation of solid sulfur. The strategic design of electrocatalysts with enhanced electrochemical activity and improved sulfur tolerance is thereby crucial to fully harness the benefits of the SOR. In this work, we developed nickel sulfide nanorods decorated with nickel nitride nanoparticles directly grown on conductive nickel foam as an efficient trifunctional electrocatalyst for the SOR, oxygen evolution reaction (OER), and hydrogen evolution reaction (HER). The SOR coupled HER approach with the developed electrocatalyst has the ability to reduce the energy consumption by 59.22%, which can make rigorous, economically viable H2 production driven by solar energy.

Single-atom metal-based electrocatalysts offer extended advantages by maximizing the utilization of active sites but often suffers from complex synthesis processes and low-density metal loading. The present work showcases a strategic design of integrating highly dense cobalt-copper dual atoms dispersed on a nitrogen-rich porous carbon network (CoCu-NGC). Atomically disperse CoCu-NGC outperforms the ORR and OER activities of single metallic counterparts (Co-NGC or Cu-NGC) and the conventional noble metal based electrocatalysts (Pt/C and RuO2). Benefitting from the electronic modulation in dual SAC system, CoCu-NGC displayed outstanding bifunctional performance with low ΔE value of 0.69 V in freshwater and that of 0.78 V in seawater, highlighting it as a potential alternate to the costly state-of-art electrocatalyst.
78.
Nibedita Sinha, Chandni Das, Santanu Pal, Rajashri Urkude, Tanbir Ahmed, Biplab Ghosh, Poulomi Roy*
Atomically Dispersed Co-Cu Dual Active Sites in Carbon Networks as Efficient Oxygen Electrocatalyst
Dalton Transactions, 2025, 10.1039/D5DT01807B (IF: 3.3)
75.
Ekta Chaturvedi* and Poulomi Roy*
Tailoring Ionic Salt in Chitosan-Activated Carbon-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Enhanced Mechanical Energy Harvesting
ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2024, 7, 9735–9745 (IF: 6.4)
A collaborative work
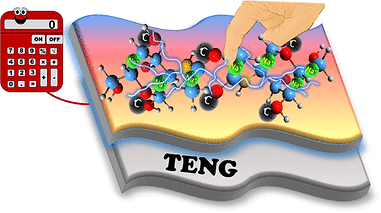
Triboelectric nanogenerators (TENGs) have emerged as an innovative approach for sustainable energy harvesting. These devices can convert mechanical energy, such as the motion of a person or the flow of water, into electrical energy through the combined principles of the triboelectric effect and electrostatic induction. Herein, we report the combination of biodegradable chitosan (CS) and waste dry leaves waste-derived activated carbon (AC) composite films as an effective tribo layer, which upon incorporation of NaCl as an ionic salt induces an impeccable ionic and interfacial polarization within the layer, leading to enhanced charge generation and transfer, thereby boosting the overall performance of the TENG. The developed TENG was also explored in practical applications by powering small electronic devices, like a calculator and a watch, along with evaluating its efficiency in harvesting mechanical energy from different human motions.
76.
S.K. Dubey, S. Pal, B. Biswas, A. Chatterjee, K. Patra, R. Mondal, A.S. Patra, M.C. Majee, S. Samanta,* P. Roy,* S. Bhattacharjee,*R. Saha*
Solvothermal synthesis of a Fe14 cluster with electrocatalytic HER activity under heterogenous condition
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 136, 2025, 40-48 (IF: 7.2)
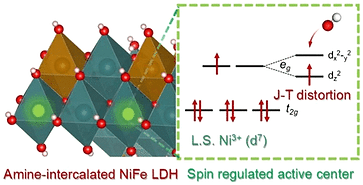
The manipulation of the valence state along with electronic spin configurations of metal sites in NiFe layered double hydroxides has been recognized as a feasible strategy to boost intrinsic electrocatalytic oxygen evolution reaction activity. In this study, high-valence Ni3+ with a low-spin configuration has been introduced in NiFe layered double hydroxide nanosheets by facile amine intercalation in the interlayers. The influence of such valence state regulations with a favorable electronic low-spin configuration of Ni3+ was found to be very impactful toward an efficient water oxidation mechanism. The electrocatalyst exhibited an outstanding OER activity and further explored toward seawater oxidation, demonstrating it to be a potential candidate with an outstanding durability of over 160 h at a high current density of 500 mA cm–2 in alkaline real seawater.
74.
S. Khatun, P. Roy*
Valence State Regulated Nickel Iron Layered Double Hydroxides by Amine Intercalation as Efficient Electrocatalysts for Seawater Oxidation
ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2024, 7, 9110–9120 (IF: 6.4)
74b.
Front Cover Page
S. Khatun, P. Roy*
Valence State Regulated Nickel Iron Layered Double Hydroxides by Amine Intercalation as Efficient Electrocatalysts for Seawater Oxidation
ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2024, 7, 9110–9120 (IF: 6.4)
The spin state regulated active center generation in the NiFe layered double hydroxide by amine intercalation has been recognized as a novel strategy not only to boost up electrocatalytic seawater oxidation, but also has the ability to hinder chlorides, offering a sustainable process.

In Journals
73.
Sakila Khatun, Koji Shimizu, Santanu Pal, Saikat Nandi, Satoshi Watanabe and Poulomi Roy*
Enthralling Anodic Protection by Molybdate on High-Entropy Alloy-Based Electrocatalyst for Sustainable Seawater Oxidation
Small, 2024, 2402720 (IF: 13.3)

Efficient and sustainable seawater electrolysis is still limited due to the interference of chloride corrosion at anode. The designing of suitable electrocatalyst is one of the crucial ways to boost electrocatalytic activity. However, the approach may fall short as achieving of high current density often occurs in CER dominating potential region. Thereby, apart from developing OER-active high-entropy alloy based electrocatalyst, the present study also offers a unique way to protect anode surface under high current density or potential by using MoO42— as effective inhibitor during seawater oxidation.The wide variation of d-band center of high-entropy alloy based electrocatalyst allows great OER proficiency exhibiting overpotential of 230 mV at current density of 20 mA cm-2. Besides, the electrocatalyst demonstrated impressive stability over 500h at high current density of 1 A cm-2 or at high oxidation potential of 2.0V vs. RHE in presence of molybdate inhibitor. Theoretical and experimental studies revealed MoO42- electrostatically accumulated at anode surface due to higher adsorption ability and thereby creating protective layer against chlorides without affecting OER.
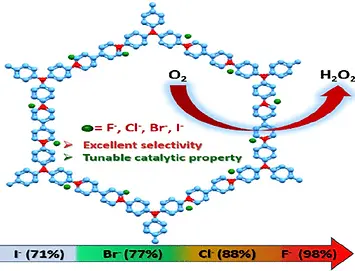
72.
S. Sarkar, N. Sinha, R. Munjal, A. Chakraborty, P. Roy*, S. Mukhopadhyay*
Exploring Counter Anions in a Redox-Active Viologen-Based Ionic Porous Organic Polymer (iPOP) for Selective Reduction of Oxygen to H2O2
ACS Applied Engineering Materials, 2024, 2, 2000–2006 (IF: 3.5)
Hydrogen peroxide, an environmentally friendly oxidant, is in high demand in various industrial sectors. Electrochemical H2O2 production by 2e– reduction of O2 is a suitable and greener alternative to the traditional anthraquinone process. However, developing metal-free electrocatalysts that predominantly follow the 2e– reduction process over the more favorable 4e– reduction is challenging. Here, we report a viologen-based redox-active ionic porous organic polymer (iPOP-TAPA-Cl) toward selective production of H2O2 (86%) electrocatalytically. By varying the counteranion (Cl–) with other halogen anions (F–, Br–, and I–), a maximum H2O2 selectivity of 98.5% with exceptional current efficiency was achieved in the case of iPOP-TAPA-F.
71.
E. Chaturvedi, P. Roy, R. Upadhyay, P. Chowdhury
Enhanced yield and production of aromatics rich fractions in bio-oil through co-pyrolysis of waste biomass and plastics
Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 178, 2024, 119106379 (IF: 6.0)
69.
Santanu Pal, Sakila Khatun and Poulomi Roy*
High Entropy Layered Hydroxide for Efficient and Sustainable Seawater Oxidation
Materials Advances, 2024, 5, 5156-5166 (IF: 5.2)

An Invited Article published under themed collection of 'Surface Engineering of Transition Metal-based 2D Layered Materials'
High entropy layered hydroxides with different compositions, unique layered structure and high mixing entropy have the potential to act as efficient as well as sustainable electrocatalyst for direct seawater splitting. Here, we report development of novel high entropy NiCrCoFeMo layered hydroxide (HE-LH) material by single step hydrothermal method, which found to be superior than its quaternary and ternary counterparts due to the availability of larger number of electroactive sites and better chloride restricting ability by interlayer anions. The HE-LH achieved 100 mA cm-2 current density at only 242, 258 and 281 mV overpotentials in 1M KOH, 1M KOH + seawater and 6M KOH + seawater, respectively. The robustness due to anti-corrosive ability of HE-LH has also been explored in highly alkaline (6M KOH) real seawater which showed over 140 h long stability at operating current density of 500 mA cm-2. The generation of β-NiOOH, also as active sites, during prolonged electrooxidation process in seawater based electrolyte found to be beneficial to maintain such highly active performances. The combination of HE-LH with Pt/C in a two electrode system also offered high current density of 500 mA cm-2 at cell voltage of only 1.92 V in highly alkaline (6M KOH) real seawater electrolyte and exhibited 50h long stability. Having such great performances, the developed novel HE-LH is believed to have potential to practically explore in seawater electrolyser.
68.
Sakila Khatun, Santanu Pal and Poulomi Roy*
Surface oxygen vacancy engineering of Cr-doped FeNi3/NiFe2O4 Mott-Schottky heterojunction as efficient electrocatalyst for high current density water oxidation
Jounal of Alloys and Compounds 2024, 977, 173393 (IF: 6.371)

70.
Tanbir Ahmed, Sakila Khatun, Sukanya Bhattacharjee and Poulomi Roy*
High-Entropy Borate as an Active Electrocatalyst for Boosted Alkaline Seawater Oxidation
ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2024, 7, 3858–3865 (IF: 6.4)
Developing efficient and stable electrocatalysts for seawater oxidation at high current density still remains challenging due to chlorine evolution reaction at the anode. Herein, we report the facile synthesis of amorphous high-entropy borate by the chemical reduction method and identify it as a very active and robust electrocatalyst for freshwater oxidation as well as seawater oxidation. The developed high-entropy borate needs only 275 and 288 mV overpotentials in 1 M KOH and 1 M KOH + seawater, respectively, to achieve a high current density of 100 mA cm–2 and exhibits outstanding stability at such a high current density for over 50 h in alkaline real seawater.

The defect engineering at the surface by filling of oxygen vacancies during OER causing surface reconstruction is considered to be a unique way to boost up intrinsic electrocatalytic activity, especially towards oxygen evolution reaction (OER) mechanism. The present study aimed creation of large number of oxygen vacancies by Cr-doping into FeNi3/NiFe2O4 Mott-Schottky heterojunction electrocatalyst causing much desirable surface engineering and electronic modulation in favour of OER activity. The optimized heterojunction nanoparticles exhibited an excellent catalytic activity with low overpotential of 246 mV at the current density of 20 mA cm-2 with low Tafel slope value of 55 mV dec-1 for OER. Such oxygen vacancy-aided surface reconstruction during OER demonstrated an outstanding durability over 200 h even at high current density of 1000 mA cm-2 in 1 M KOH electrolyte. The surface oxygen vacancy engineering with the help of ex-situ Raman spectroscopy at different anodic potentials reveals the filling of vacancies and generation of MOOH as surface reconstruction of electrocatalyst during OER, also supported by XPS, TEM and EELS analyses.

Replacing sluggish anodic oxygen evolution reaction by hydrazine oxidation reaction in seawater electrolysis is one of the smartest ways of getting multiple benefits as it offers an energy saving route for hydrogen production keeping the cell voltage way smaller than responsible voltage for corrosive chloride oxidation. Here, we report iron-doped Co3N as highly active electrocatalyst towards hydrazine oxidation reaction and hydrogen evolution reaction in wide pH range of 7–14. The two-electrode electrolyser system reached industry scale current density of 1000 mA cm−2 at ultralow cell voltage of 0.65 V, and found sustainable at 500 mA cm−2 over 95 h in hydrazine assisted alkaline seawater splitting. The electrolyser system also achieved 200 mA cm−2 current density at 0.75 V in hydrazine assisted neutral seawater medium. Interestingly, a thin amorphous iron oxide layer formed in Fe-doped Co3N provided much needed protection during electrocatalysis offering long term stability at industry level current density.
67.
Nibedita Sinha, Chandni Das and Poulomi Roy*
Iron-doped cobalt nitride as an efficient electrocatalyst towards energy saving hydrazine assisted seawater splitting in near neutral to highly alkaline pH achieving industry level current density
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy 2023, 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2023.10.299 (IF: 7.2)

Tweeted by IC
66.
Chandni Das, Nibedita Sinha and Poulomi Roy*
Defect Enriched Tungsten Oxide Phosphate with Strategic Sulfur Doping for Effective Seawater Oxidation
Inorganic Chemistry, 2023, 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.3c03212 (IF: 5.436)
The intrinsic ability of defects within the electrocatalysts can be judiciously utilized in designing robust electrocatalysts for efficient seawater oxidation. Herein, we have fabricated a novel tungsten oxide phosphate (W12PO38.5) with optimized sulfur doping triggering the insertion of a large number of defect sites. This allows for boosted OER performance in alkaline freshwater as well as seawater, avoiding the unwanted chlorine evolution reaction. The optimized electrocatalyst achieved high current densities of 500 mA cm–2 at an overpotential of just 387 mV in fresh water and 100 mA cm–2 at 380 mV in alkaline seawater for OER. Besides the excellent catalytic performances, the developed electrocatalyst appeared to be a durable catalyst as well. An interesting electrocatalytic activation caused by the generous electronic redistribution led the electrocatalyst to achieve great stability over 100 h at a 100 mA cm–2 current density in alkaline real seawater.
65.
Santanu Pal, Tanbir Ahmed, Sakila Khatun and Poulomi Roy*
Heterojunction Engineering for Electrocatalytic Applications
ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2023, 6, 7737–7784 (IF: 6.4)
65b.
Front Cover Page
Santanu Pal, Tanbir Ahmed, Sakila Khatun and Poulomi Roy*
Heterojunction Engineering for Electrocatalytic Applications
ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2023, 6, 7737–7784 (IF: 6.4)
The combination of rationally chosen materials with different band structures offers a self-driven electron flow, creating an electrophilic/nucleophilic region at the interface. Such charge separation at the interface facilitates adsorption of small molecules, especially H2O, urea, hydrazine, biomass molecules, etc., driving electrocatalytic reactions and thereby producing value-added products and clean fuels.

64.
Tanbir Ahmed, Sukanya Bhattacharjee and Poulomi Roy*
Amorphous vanadium-doped cobalt oxyborate as an efficient electrocatalyst for urea-assisted H2 production from urine sewage
Dalton Transactions, 2023, 52, 9546-9552 (IF: 4.0)
Invited Review
Production of green hydrogen from the electrolysis of water is considered to be one of the most desirable processes to address the clean energy demand. However, a high energy barrier and an economically unsustainable nature limit the process toward practical implementation in an extensive way. The designing of an electrocatalyst accompanied by defect engineering, heteroatom doping, and strain creation are known to be effective strategies to make the process efficient. Recently, construction of heterojunctions with a combination of materials with desired band structures is considered to be a smart approach in promoting electrocatalytic activities by attaining charge redistribution and manipulating the electronic structure at the interface. The present review elaborately discusses possible heterojunctions, alterations at the interface, insight thermodynamics, and possible causes for boosting electrocatalytic activities. The heterojunction-based electrocatalysts are found not only effective for oxygen evolution reactions and hydrogen evolution reactions, but also to be very useful toward various electrochemical oxidation reactions as well as electrochemical reduction reactions involving small molecules undergoing decomposition at very low energy. Having such a specialty, there is no doubt that heterojunction-based electrocatalysts are going to be the primary choices of researchers in coming years.


The urea oxidation reaction (UOR) with low required oxidation potential is not only an energy-saving strategy for efficient hydrogen production but also offers an effective way to treat wastewater by decomposing urea. An amorphous cobalt oxyborate with optimum vanadium doping has been identified as an efficient electrocatalyst for UOR for the first time with great stability. The electrocatalyst requires only 1.37 V potential to achieve a current density of 20 mA cm−2. Impressively, the developed electrocatalyst exhibited very active and long stability in alkaline raw bovine urine as extreme urine sewage media coupled with efficient hydrogen production at the cathode.
Selected as Hot Paper
63.
Santanu Pal, Koji Shimizu, Sakila Khatun, Soumen Singha, Satoshi Watanabe* and Poulomi Roy*
Electrolyte Engineering for Effective Seawater Splitting Based on Manganese Iron Chromium Layered Triple Hydroxides as Novel Bifunctional Electrocatalysts
Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2023, 11, 12151-12163 (IF: 14.511)

Seawater splitting remain far-fetched due to interference of corrosive chlorine evolution reaction at anode. The lowering of overpotential with the help of effective electrocatalyst is one way to deal with it. However, to achieve hydrogen production under high current, practically potential above 2.0 V needs to be applied, which is electrochemically chloride oxidation dominating region. In this report, we show that the presence of trace amount of anionic inhibitor, especially carbonate, provide a much-needed anionic protective layer at anode surface, selectively restricting chlorides but allowing hydroxides to reach the anode surface. The hypothesis has been examined on novel MnFeCr layered triple hydroxides as bifunctional electrocatalyst. The developed electrocatalyst exhibits overpotential of 242 mV for OER and 154 mV for HER at benchmarking current density of 10 mA cm-2. Theoretical calculations establish the possible OER pathways and explains reason for good electrocatalytic activity of developed electrocatalyst. Having such electrocatalytic activity, in alkaline real seawater the electrocatalyst in presence of carbonate inhibitor shows an impressive stability over 500 h maintaining the cell potential of 2.2 – 2.3 V without showing any sign of electrode degradation. The findings thereby provide much-needed solution to make seawater splitting feasible for sustainable hydrogen production.
Invited Research Article

62.
Sakila Khatun , Santanu Pal , Nibedita Sinha , Chandni Das , Tanbir Ahmed and Poulomi Roy*
New Age Chloride Shielding Strategies for Corrosion Resistant Direct Seawater Splitting
Chemical Communications, 2023, 59, 4578-4599 (IF: 6.065)
Electrocatalytic direct seawater splitting is considered to be one of the most desirable and necessitous approach to produce substantial amount of green hydrogen to meet the energy demand. However, practically seawater splitting remains far-fetched due to electrochemical interference of multiple elements present in seawater, among which chlorine chemistry is the most aggravating one, causing severe damages to the electrodes. To overcome such limitations, apart from robust electrocatalyst design, electrolyte engineering along with in depth corrosion engineering are essential aspects, which needs to be thoroughly judged and explored. Indeed, extensive studies and various approaches including smart electrolyser design have been attempted in last couple of years on this matter. The present review offers a comprehensive discussion on various strategies to achieve effective and sustainable direct seawater splitting avoiding chlorine electrochemistry to achieve industry level performances.
Invited Feature Article
61b.
Front Coverpage
on
Nibedita Sinha and Poulomi Roy*
Nickel–Vanadium–Manganese Trimetallic Nitride as Energy Saving, Efficient Bifunctional Electrocatalyst for Alkaline Water Splitting via Urea Electrocatalysis
Urea is often found in wastewater collected from agricultural or fertilizer industry runoff, causing concern due to its toxicity. The newly developed trimetallic nickel vanadium manganese nitride has efficient ability to act as a bifunctional electrocatalyst for economic hydrogen production via urea assisted water splitting decomposing urea into N2 and CO2.

61.
Nibedita Sinha and Poulomi Roy*
Nickel–Vanadium–Manganese Trimetallic Nitride as Energy Saving, Efficient Bifunctional Electrocatalyst for Alkaline Water Splitting via Urea Electrocatalysis
Inorganic Chemistry, 2023, 62, 3349-3357 (IF: 5.436)
The trimetallic nickel vanadium manganese nitride porous microspheres have been developed as efficient bifunctional electrocatalyst for hydrogen production via urea assisted water splitting.
Tweeted by IC

60.
Sakila Khatun and Poulomi Roy*
Mott-Schottky Heterojunction of Se/NiSe2 as Bifunctional Electrocatalyst for Energy Efficient Hydrogen Production via Urea Assisted Seawater Electrolysis
Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2023, 844-854 (IF: 9.965)

Seawater electrolysis is considered to be very challenging owing to competitive reaction kinetics in between oxygen evolution reaction and corrosive chlorine evolution reaction mechanism at anode, especially towards higher current density. The present work, proposes a promising and energy efficient strategy by coupling seawater splitting with urea decomposition lowering oxidation potential and thereby avoiding hypochlorite formation even at high current density. The rational design of Mott-Schottky heterojunction of Se/NiSe2 as electrocatalyst is considered to be highly effective in this regard. The developed Se/NiSe2 exhibits extraordinary energy saving for alkaline seawater splitting in presence of urea. The Se/NiSe2/NF || Se/NiSe2/NF electrolyser configuration achieved 10 and 50 mAcm−2 current densities with cell voltage of 1.59 and 1.70 V along with outstanding operational durability over 50 h. The large number of carrier density generates by synergistic self-driven electron transfer from Se to NiSe2 at the heterojunction, unique metallic properties of selenium (Se), and also abundance accessible reactive edges on the porous channel of Ni foam are believed to be the reason behind such enhanced electrocatalytic activities towards urea oxidation reaction and hydrogen evolution reaction offering unique and much energy saving approach for alkaline-urea-seawater electrolysis avoiding hypochlorite formation.

59.
Chandni Das, Nibedita Sinha and Poulomi Roy*
Transition Metal Non-Oxides as Electrocatalysts: Advantages and Challenges
Small, 2022, 2202033 (IF: 15.153)
In the pursuit of noble metal-free electrocatalysts, transition metal nonoxides, having diversities in their structures, phases, electronic configurations, corrosion-resistant nature, and exposed active site-rich surfaces, have attracted much attention in the past few years. State-of-the-art progress on their electrocatalytic activities toward oxygen evolution reactions, hydrogen evolution reactions, and oxygen reduction reactions is addressed in this review.

58.
Chandni Das and Poulomi Roy*
Cobalt and Iron Phosphates with Modulated Compositions and Phases as Efficient Electrocatalysts for Alkaline Seawater Oxidation,
Chemical Communications, 58, 2022, 6761-6764 (IF: 6.065)
Electrocatalyst serving for both fresh water and real seawater electrolysis is very limited. In this work, we have developed series of iron-tuned cobalt phosphates and cobalt-tuned iron phosphate solid solutions as electrocatalysts exhibiting excellent OER activities not only in freshwater but also in alkaline real seawater with Faradaic efficiency of 95%.

57b.
Inside Front Coverpage
on
Sakila Khatun and Poulomi Roy*
Cobalt chromium vanadium layered triple hydroxides as an efficient oxygen electrocatalyst for alkaline seawater splitting

57.
Sakila Khatun and Poulomi Roy*
Cobalt chromium vanadium layered triple hydroxides as an efficient oxygen electrocatalyst for alkaline seawater splitting,
Chemical Communications, 2022, 58, 1104-1107 (IF: 6.065)
Cobalt chromium vanadium layered triple hydroxides have been identified as a promising electrocatalyst for seawater splitting. The insertion of vanadium as a third metal into cobalt chromium layered double hydroxides not only adds extra cationic active sites but also facilitates electronic transition from Co(II) to V(V) boosting the OER activity and suppressing the CER.
Tweeted by ChemComm

56.
Sakila Khatun, Koji Shimizu, Soumen Singha, Rajat Saha, Satoshi Watanabe* and Poulomi Roy*
Defect Enriched Hierarchical Iron Promoted Bi2MoO6 Hollow Spheres as Efficient Electrocatalyst for Water Oxidation
Chemical Engineering Journal, 426, 2021, 131884 (IF: 16.744)
The manipulation in crystal structure as well as electronic structure of material apart from the morphology play important role in determining electrocatalytic activity. Bismuth molybdate with its special layered structure in orthorhombic phase and hollow sphere morphology performed as potential electrocatalyst for oxygen evolution reaction in alkaline medium. The activity can further be enhanced by promoting iron in the crystal structure. The strain as well as dislocation developed in the crystal structure of Bi2MoO6 upon iron incorporation are well- studied. The presence of optimum amount of iron and thereby creating oxygen vacancies have been found to be beneficial, though higher concentration turns out to be detrimental for the electrocatalytic performance. The optimum iron promoted Bi2MoO6 leads to achieve overpotential value of 286 mV at 10 mA cm-2 current density with Tafel slope of only 44 mV dec-1 for OER. The experimental results are well-supported by the density functional theory simulations, which demonstrate that iron incorporation lowers the energy barrier by promoting the adsorptions of OER intermediates, most distinctly the oxygen adsorption.
55.
M Prudhvi Krishna, Simeon A Babalola, Samik Dutta, Shitanshu Shekhar Chakraborty, Murugan Thangadurai, Himadri Roy, Nilrudra Mandal, Harish Hirani,* and Poulomi Roy*
Effectiveness of different facemask materials to combat transmission of airborne diseases
Sādhanā, 46, 2021, 119 (IF: 1.188)
Research work related to COVID 19

54.
S. Khatun, H. Hirani, P. Roy*
Seawater electrocatalysis: activity and selectivity
Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 9, 2021, 74-86 (IF: 14.511)
Seawater is considered to be a major hydrogen reservoir. However, the presence of multielements in seawater and their interference in electrochemistry, especially the chlorine chemistry, makes the electrocatalytic water splitting of seawater very challenging and still not completely understandable. To make seawater electrolysis sustainable, the activity of electrocatalysts may not be the only parameter, but the selectivity of the efficient oxygen evolution reaction suppressing the corrosive chlorine chemistry is highly desirable. Thereby, the current review not only focuses on fundamentals to understand the mechanisms involved in the anode and cathode, but also discusses different electrocatalysts, factors affecting their performance, and finally the rational design of electrolyzers finding the possibilities towards commercialization.

53.
S. Khatun, P. Roy*
Bismuth Iron Molybdenum Oxide Solid Solutions: A Novel and Durable Electrocatalyst for Overall Water Splitting,
Chemical Communications, 56, 2020, 7293-7296 (IF: 6.065)
The drive for finding active bifunctional electrocatalysts for effi- cient overall water splitting continues in order to extract energy in the form of hydrogen as a clean fuel. Bismuth iron molybdenum oxide solid solution, composed of orthorhombic Bi2MoO6 as the major component and monoclinic Bi3(FeO4)(MoO4)2 as the minor component, has been identified as a potential electrocatalyst for the first time.
52.
S Samanta, P Roy, P Kar
Sensing of ethanol and other alcohol contaminated ethanol by conducting functional poly (o-phenylenediamine)
Materials Science and Engineering: B, 256, 2020, 114541 (IF: 3.507)
51.
S Samanta, P Roy, P Kar
Sensing of Higher Alcohols and Selective Sensing of Iso-amyl Alcohol by Poly (o-phenylenediamine) Nanofiber
IEEE Sensors Journal, 2020, DOI: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.2988885 (IF: 3.076)
50.
K Ghosh, S Mazumder, B Kumar Singh, H Hirani, P Roy, N Mandal,
Tribological Property Investigation of Self-Lubricating Molybdenum-Based Zirconia Ceramic Composite Operational at Elevated Temperature
Journal of Tribology, 142, 2020, 021704 (IF: 1.648)
49.
A Singh, S Samanta, N Bage, BD Ghosh, P Kar, P Roy
Synthesis of stable aqueous colloid of functionalized silver nanorod
Functional Materials Letters 12, 2019, 1950076 (IF: 1.622)
48.
Shipra Raj, Sengeni Anantharaj, Subrata Kundu*, Poulomi Roy*
In Situ Mn-Doping-Promoted Conversion of Co(OH)2 to Co3O4 as an Active Electrocatalyst for Oxygen Evolution Reaction
ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2019, 7, 9690-9698. (IF: 9.224)

Revealing the intrinsic catalytic properties and their dependence on other factors is always a desired challenge in the field of catalysis. Finding and fine-tuning of the inherent electrocatalytic properties of 3D nonprecious metal hydroxides and oxides by a foreign element doping is an attractive domain in the electrocatalysis of water oxidation. This report reveals such an effect of Mn doping on the electrocatalytic oxygen evolution reaction (OER) of Co3O4 nanosheet arrays grown on nickel foam (NF) by the ammonia evaporation technique. The Mn doping induces the in situ conversion of Co(OH)2 into Co3O4 during deposition. The strain generation during doping and the presence of metallic Mn are important factors for enhanced OER performance. Such a unique way of doping as well as in situ conversion of hydroxides into oxides offer an excellent electrocatalyst with superior performance compared to pristine Co3O4 or Co(OH)2 nanoflakes.
47.
Shipra Raj, Suneel Kumar Srivastava, Pradip Kar, Poulomi Roy*
In situ Growth of Co3O4 Nanoflakes on Reduced Graphene Oxide- Wrapped Ni-foam as High Performance Asymmetric Supercapacitor,
Electrochimica Acta, 302, 2019, 327-337 (IF: 7.336)

We report an in situ reduction process of GO to rGO on Ni foam during deposition of Co3O4 nanoflakes via ammonia evaporation technique followed by thermal treatment. The synthesis procedure and the design of electrode make it very promising for supercapacitor application. The characteristic electrochemical properties indicate the ‘battery’ type material and supercapattery performances were investigated thoroughly. The electrode exhibited considerably high specific capacity of 1328 C g-1 at 2 A g-1 current density and showed good stability compared to Co3O4 nanoflakes deposited on bare Ni foam. The performance as asymmetric supercapacitor in a two-electrode configuration of Co3O4-rGO/Ni foam also revealed high specific capacitance of 80 F g!1 at current density of 0.1 A g!1 and excellent stability with 94.5% capacity retention after 10,000 cycles. A considerably high energy density of 20 Wh kg!1 at power density of 1200 W kg-1 was achieved for Co3O4-rGO/Ni foam based asymmetric device, confirming the material as a potential candidate for supercapacitor application.

46.
Shipra Raj, Pradip Kar, Poulomi Roy*
Facile Synthesis of Flower-like Morphology of Cu0.27Co2.73O4 for High-Performance Supercapattery with Extraordinary Cycle Stability
Chemical Communication, 54, 2018, 12400-12403. (IF: 6.29)
The partial replacement of Co by Cu in cobaltite to give Cu0.27Co2.73O4 with unique flower-like morphology is found to be very beneficial for supercapacitor–battery hybrid applications. The 3D architecture of the material on a conductive substrate resulted in outstanding super- capattery performance. Asymmetric assembly of the material with activated carbon in a two-electrode system delivered high energy and power densities as well as a high specific capacity. The device also showed excellent cycling stability over 20 000 cycles, with a capacity retention value of 86.9%.
45.
Mayukh Chakravarty, Anupam Das, Chitralee Sarma, Poulomi Roy*
a-Fe2O3/TiO2 Hybrids with Tunable Morphologies as Efficient Photocatalyst and Positive Electrode for Supercapacitor
Chem Select, 3, 2018, 3284-3294. (IF: Pending)
44.
Shipra Raj,† Yifan Dong,† Pradip Kar, Liqiang Mai, Song Jin, Poulomi Roy*
Hybrid NiCo2O4-NiCo2S4 Nanoflakes as High Performance Anode Materials for Lithium Ion Batteries
Chem Select, 3, 2018, 2315 – 2320. (IF: Pending)
43.
Shipra Raj, Pradip Kar, Poulomi Roy*
Ammonia-Assisted Growth of CoSn(OH)6 Nanostructures and Their Electrochemical Performances for Supercapacitor,
J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol., 18, 2018, 1-7 (DOI: 10.1166/jnn.2018.15829) (IF: 1.509).
42.
Indranil Mondal, Shipra Raj, Poulomi Roy, Raju Poddar,
Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPs) as contrast agent for imaging of animal tissue using swept source optical coherence tomography (SSOCT),
Laser Physics, 28, 2018, 015601 (IF: 1.102).
41.
S. Raj, S. Kumar, S.K. Srivastava, P. Kar, P. Roy*
Deposition of Tin Oxide Thin Films by SILAR Method and Its Characterization
Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 2018, 18, 2569-2575. (IF: 1.509)
40.
Shipra Raj , Suneel Kumar Srivastava , Pradip Kar and Poulomi Roy*
Three-dimensional NiCo2O4/NiCo2S4 Hybrid Nanostructures on Ni-foam as High-performance Supercapacitor Electrode,
RSC Advances, 2016, 6, 95760-95767(IF: 3.289; Citation: 7)
39.
S. Samanta, P. Roy, P. Kar,
Influence of structure of poly(o-phenylenediamine) on the doping ability and conducting property,
Ionics, 2017, 23, 937-947 (IF: 2.17).
38.
S. Samanta, P. Roy, P. Kar,
Synthesis of poly(o-phenylenediamine) nano-fiber with novel structure and properties,
Polymers for Advanced Technologies, 2016, 28, 797–804 (IF: 2.007).
37.
Shalini Divya, Remith Pongilat, Tapas Kuila, Kalaiselvi Nallathamby, Suneel Kumar Srivastava, Poulomi Roy*
Spinel-Structured NiCo2O4 Nanorods as Energy Efficient Electrode for Supercapacitor and Lithium Ion Battery Applications
Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 2016, 16, 9761-9770 (IF: 1.554).
36.
Siddhartha Samanta, Poulomi Roy, Pradip Kar,
Structure and Properties of Conducting Poly(o-phenylenediamine) Synthesized in Different Inorganic Acid Medium,
Macromolecular Research, 2016, 24, 342-349 (IF: 1.597).

35.
Poulomi Roy* and Suneel Kumar Srivastava*
Nanostructured Anode Materials for Lithium Ion Batteries
Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 3, 2015, 2454-2484
(IF: 14.511; Citation: 456) Selected as Hot Paper 2015
High-energy consumption in our day-to-day life can be balanced not only by harvesting pollution-free renewable energy sources, but also requires proper storage and distribution of energy. In this regard, lithium ion batteries are currently considered as effective energy storage devices and involve the most active research. There exist several review articles dealing with various sections of LIBs, such as the anode, the cathode, electrolytes, electrode–electrolyte interface etc. However, the anode is considered to be a crucial component affecting the performance of LIBs as evident from the tremendous amount of current research work carried out in this area.

34.
Poulomi Roy* and Suneel Kumar Srivastava*
Nanostructured Copper Sulfides: Synthesis, Properties and Applications
CrystEngComm., 17, 2015, 7801-7815 (IF: 4.034; Citation: 94).
Among different metal chalcogenides, copper sulfides have been extensively studied in the past few years due to their semiconducting and non-toxic nature, making them useful in a wide range of applications from the energy to the biomedical fields. A series of stoichiometric compositions of copper sulfides from Cu-rich, Cu2S to Cu-deficient, CuS2 exist with different crystal structures as well as phases, resulting in different unique properties. The suitable band gap values in the range of 1.2–1.5 eV and unique optoelectronic properties indicate that the material is photocatalytically active and exhibits excellent plasmonic behavior.
33.
Ritwik Panigrahi, Poulomi Roy and Suneel Kumar Srivastava
Controlled Growth of PbSe Nanorods to Flower-like Structure and Their Size- dependent Optical Properties
Advanced Science, Engineering and Medicine, 7, 2015, 190-194
32.
Siddhartha Samanta, Poulomi Roy, Pradip Kar
Influence of pH of the reaction medium on the structure and property of conducting poly(o-phenylenediamine)
Materials Today: Proceedings, 2, 2015, 1301 – 1308.

31.
Poulomi Roy, Chitta Ranjan Das, Kiyoung Lee, Robert Hahn, Tobias Ruff, Mathias Moll, Patrik Schmuki
Oxide Nanotubes on Ti-Ru Alloys: Strongly Enhanced and Stable Photoelectrochemical Activity for Water Splitting
Journal of American Chemical Society, 133, 2011, 5629-5631
(IF: 11.44; Citation: 42)
The present work shows a significant enhance- ment of the photoelectrochemical water-splitting performance of anodic TiO2 nanotube layers grown on low concentration (0.01!0.2 at% Ru) Ti!Ru alloys. Under optimized preparation conditions (0.05 at% Ru, 450 C annealing) the water splitting rate of the oxide tubes could be 6-fold increased. Moreover, the beneficial effect is very stable with illumination time; this is in contrast to other typical doping approaches of TiO2.

30.
Poulomi Roy, Steffan Berger, Patrik Schmuki
TiO2 Nanotubes and Their Applications – A Review
Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 50, 2011, 2904-2939
(IF: 13.73; Citation: 2851)
TiO2 is one of the most studied compounds in materials science. Owing to some outstanding properties it is used for instance in photocatalysis, dye‐sensitized solar cells, and biomedical devices. In 1999, first reports showed the feasibility to grow highly ordered arrays of TiO2 nanotubes by a simple but optimized electrochemical anodization of a titanium metal sheet. This finding stimulated intense research activities that focused on growth, modification, properties, and applications of these one‐dimensional nanostructures. This review attempts to cover all these aspects, including underlying principles and key functional features of TiO2, in a comprehensive way and also indicates potential future directions of the field.
29.
Chittaranjan Das, Poulomi Roy, Min Yang, Himendra Jha, Patrik Schmuki
Nb doped TiO2 nanotubes for enhanced photoelectrochemical water-splitting
Nanoscale, 3, 2011, 3094-3096 (IF: 7.00; Citation: 32)
28.
H. Jha, P. Roy, R. Hahn, P. Schmuki
Fast formation of aligned high-aspect ratio TiO2 nanotube bundles that lead to increased open circuit voltage when used in dye sensitized solar cells,
Electrochem. Commun., 13, 2011, 302-305 (IF: 4.859; Citation: 8)
27.
T. Dey, P. Roy, B. Fabry, P. Schmuki
Anodic mesoporous TiO2 layer on Ti for enhanced formation of biomimetic hydroxyapatite
Acta Biomaterialia, 7, 2011, 1873-1879. (IF: 5.076; Citation: 23)

26.
Poulomi Roy, Tuli Dey, Kiyong Lee, Doohun Kim, Ben Fabry, Patrik Schmuki
Size-selective separation of macro-molecules by nanochannel titania membrane with self cleaning (de-clogging) ability
Journal of American Chemical Society, 132, 2010, 7893-7895
(IF: 11.44; Citation: 35)
We report on a simple and self-organizing process for the fabrication of TiO2 nanochannel membranes with a channel width of 8−10 nm that can be used for size selective separation of macromolecules (proteins). The membrane, consisting of self-aligned oxide channels, is formed by complete anodization of a thin Ti foil under specific electrochemical conditions in a glycerol-phosphate electrolyte. Due to self-cleaning properties of TiO2, clogged membranes (for example due to extended use) can easily be fully reopened and thus are reusable. As the TiO2 after anodic formation directly contains anatase crystallites (the most photoactive TiO2 crystal form) no thermal treatment of the membrane is required (avoiding the danger of thermally induced cracking).

25.
Poulomi Roy, Doohun Kim, Kiyoung Lee, Erdmann Spiecker, Patrik Schmuki
TiO2 nanotube based dye sensitized solar cell
Nanoscale, 2, 2010, 45–59 (Most accessed paper) (IF: 7.0; Citation: 333)
The article reviews the current status of using TiO2 nanotubes in Grätzel-type, dye-sensitized solar cells and extends the overview with the latest results and findings. Critical factors in tube geometry (length, diameter, top morphology), crystal structure (amorphous, anatase, rutile) as well as factors affecting dye loading or electron mobility are addressed. The highest solar cell efficiencies today for pure nanotube systems reach approximately 4% while for some mixed systems, around 7% has been reported. For both systems significant room for enhancement is anticipated and some key points and strategies for improvement are outlined.
24.
Poulomi Roy, Tuli Dey, Patrik Schmuki
Scanning Electron Microscopy Observation of Nanoscopic Wetting of TiO2 Nanotubes and ODS Modified Nanotubes Using Ionic Liquids
Electrochemistry Solid State Letters 13(7), 2010, E11-E13 (IF: 1.967; Citation: 13)
23.
Yan Yan Song, Poulomi Roy, Indhumati Paramasivam, Patrik Schmuki
Voltage induced payload release and wettability control on TiO2 and TiO2 nanotubes
Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 49, 2010, 351-354 (selected as Hot paper) (IF: 13.73; Citation: 14)
22.
S.P. Albu, P. Roy, S. Virtanen, P, Schmuki, TiO2 nanotubes: Critical factors of anodic growth of nanotubes
Israel Journal of Chemistry, 50, 2010, 453-467 (IF: 0.794; Citation: 26).
21.
D. Kim, P. Roy, K. Lee, P. Schmuki, Dye-sensitized solar cells using anodic TiO2 mesosponge: Improved efficiency by TiCl4 treatment
Electrochem. Commun. 12, 2010, 574-578 (IF: 4.282; Citation: 50).
20.
Kiyong Lee, Doohun Kim, Poulomi Roy, Balaji I. Birajdar, Erdmann Spiecker, and Patrik Schmuki
Anodic Formation of Thick Anatase TiO2 Mesosponge Layers for High-Efficiency Photocatalysis
Journal of American Chemical Society, 132, 2010, 1478-1479 (IF: 11.44; Citation: 84).
19.
Steffen Berger, Robert Hahn, Poulomi Roy, Patrik Schmuki
Self-organized TiO2 nanotubes: Factors affecting their morphology and properties
Physica Status Solidi B, 247, 2010, 2424-2435 (IF: 1.344; Citation: 18).
18.
Wonjoo Lee, Doohun Kim, Kiyoung Lee, Poulomi Roy, Patrik Schmuki
Direct anodic growth of thick WO3 mesosponge layers and characterization of their photoelectrochemical response
Electrochimica Acta, 56, 2010, 828-833 (IF: 3.642; Citation: 20).
17.
Doohun Kim, Kiyong Lee, Poulomi Roy, Balaji I. Birajdar, Erdmann Spiecker, and Patrik Schmuki
Formation of a Non-Thickness-Limited TiO2 Mesosponge and its Use in Dye sensitized solar cells
Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 48, 2009, 9326-9329 (Selected as Hot paper) (IF: 13.73; Citation: 30).
16.
Poulomi Roy, Doohun Kim, Indhumati Paramasivam, Patrik Schmuki
Improved efficiency of TiO2 nanotubes in dye sensitized solar cells by decoration with TiO2 nanoparticles
Electrochemistry Communications, 11, 2009, 1001-1004 (IF: 4.243; Citation: 112).
15.
Poulomi Roy, Robert Lynch, Patrik Schmuki
Electron beam induced in-vacuo Ag deposition on TiO2 from ionic liquids
Electrochemistry Communications, 11, 2009, 1567-1570 (IF: 4.243; Citation: 13).
14.
Yan-Yan Song, Robert Lynch, Doohun Kim, Poulomi Roy, and Patrik Schmuki
TiO2 Nanotubes: Efficient Suppression of Top Etching during Anodic Growth
Electrochemical and Solid-State Letters, 12(7), 2009, C17-C20 (IF: 1.837; Citation: 25).
13.
A. Benoit, I. Paramasivam, Y.-C. Nah, P. Roy, P. Schmuki
Decoration of TiO2 nanotube layers with WO3 nanocrystals for high electrochromic activity
Electrochemistry Communications, 11, 2009, 728-732 (IF: 4.243; Citation: 46)
12.
I. Serebrennikova, I. Paramasivam, P. Roy, W. Wei, S. Virtanen and P. Schmuki
Steel corrosion in alkaline batteries
Electrochimica Acta, 54, 2009, 5216-5222 (IF: 3.325; Citation: 1)
11.
Poulomi Roy, Kamalesh Mondal and Suneel K. Srivastava
Synthesis of Twinned CuS Nanorods by Simple Wet Chemical Method
Crystal Growth & Design, 2008, 8(5), 1530-1534 (IF: 4.215; Citation: 40)
10.
Kamalesh Mondal, Poulomi Roy and Suneel K. Srivastava
Facile Biomolecule-Assisted Hydrothermal Synthesis of Trigonal Selenium Microrods
Crystal Growth & Design, 2008, 8(5), 1580-1584 (IF: 4.215; Citation: 15).
9.
Jyotiranjan Ota, Poulomi Roy, Suneel Kumar Srivastava, B.B. Nayak and A. K. Saxena
Morphology Evolution of Sb2S3 under Hydrothermal conditions: Flower like Structure to Nanorods
Crystal Growth & Design, 2008, 8(6), 2019-2023 (IF: 4.215; Citation: 24).
8.
Poulomi Roy and Suneel Kumar Srivastava
Solvothermal growth of flower-like morphology from nanorods of copper sulfides
Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 2007, 8(3), 1523–1527 (IF: 1.927; Citation: 10).
7.
Poulomi Roy and Suneel Kumar Srivastava
Synthesis and characterization of Copper sulfide nanorods by soft chemical method
Materials Letters, 61, 2007, 1693-1697 (IF: 1.3; Citation: 36).
6.
Poulomi Roy and Suneel Kumar Srivastava
Hydrothermal growth of CuS nanowires from Cu-dithiooxamide, a novel single source precursor
Crystal Growth and Design, 6(8), 2006, 1921-1926 (Most accessed article) (IF: 4.046; Citation: 78).

CuS nanowires have been successfully prepared from Cu−dithiooxamide, a novel single-source precursor, by a hydrothermal method at 120 °C for 24 h. The nanowires are 40−80 nm in diameter and up to a few microns long, and a possible reaction mechanism of their formation is proposed. The effects of reaction temperature, duration, and solvents also were studied. X-ray diffraction patterns showed the formation of a covellite form of CuS having a hexagonal phase under hydrothermal conditions. The morphology of the products was studied by scanning electron microscopy and transmission electron microscopy. The composition and purity of products were examined by energy-dispersive X-ray analysis and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Optical studies of the products also were carried out.
5.
Poulomi Roy and Suneel Kumar Srivastava
In situ Sn-doping of CdS thin film in chemical bath its characterization
Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 39, 2006, 4771-4776 (IF: 2.064; Citation: 19)
4.
Poulomi Roy, Suneel Kumar Srivastava
A New Approach towards the Growth of Cadmium Sulphide Thin Film by CBD Method and Its Characterization
Materials Chemistry and Physics, 95, 2006, 235–241 (IF: 1.414; Citation: 46).
3.
Poulomi Roy, Suneel Kumar Srivastava
Chemical bath deposition of MoS2 thin film using (NH4)2MoS4 as a single source for molybdenum and sulphur
Thin Solid Films, 496, 2006, 293–298 (IF: 1.732; Citation: 23).
2.
Poulomi Roy, Jyoti Ranjan Ota, Suneel Kumar Srivastava
A new route for preparing crystalline ZnS thin films by chemical bath deposition method and its characterization
Thin Solid Films, 515 (4), 2006, 1912-1917 (IF: 1.732; Citation: 64).
1.
Jyoti R. Ota, Poulomi Roy, Suneel Kumar Srivastava, R. Popovitz-Biro and Reshef Tenne
Simple hydrothermal method for the growth of Bi2Se3 nanorods
Nanotechnology, 17 (6), 2006, 1700-1705 (IF: 3.652; Citation: 17).
